Metabolism of adipose tissue
Adipocytes have a crucial role in energy homeostasis and metabolism due to their role as most important energy storage in mammals. While white adipocytes store excess energy as fat, so called brown adipocytes are specialized to consume energy and produce heat in a process termed non-shivering thermogenesis, which is essential to keep newborn mammals warm. Importantly, recent findings not only showed that also human adults possess metabolically active brown fat, but that its abundance and activity is positively correlated with cardiovascular health.
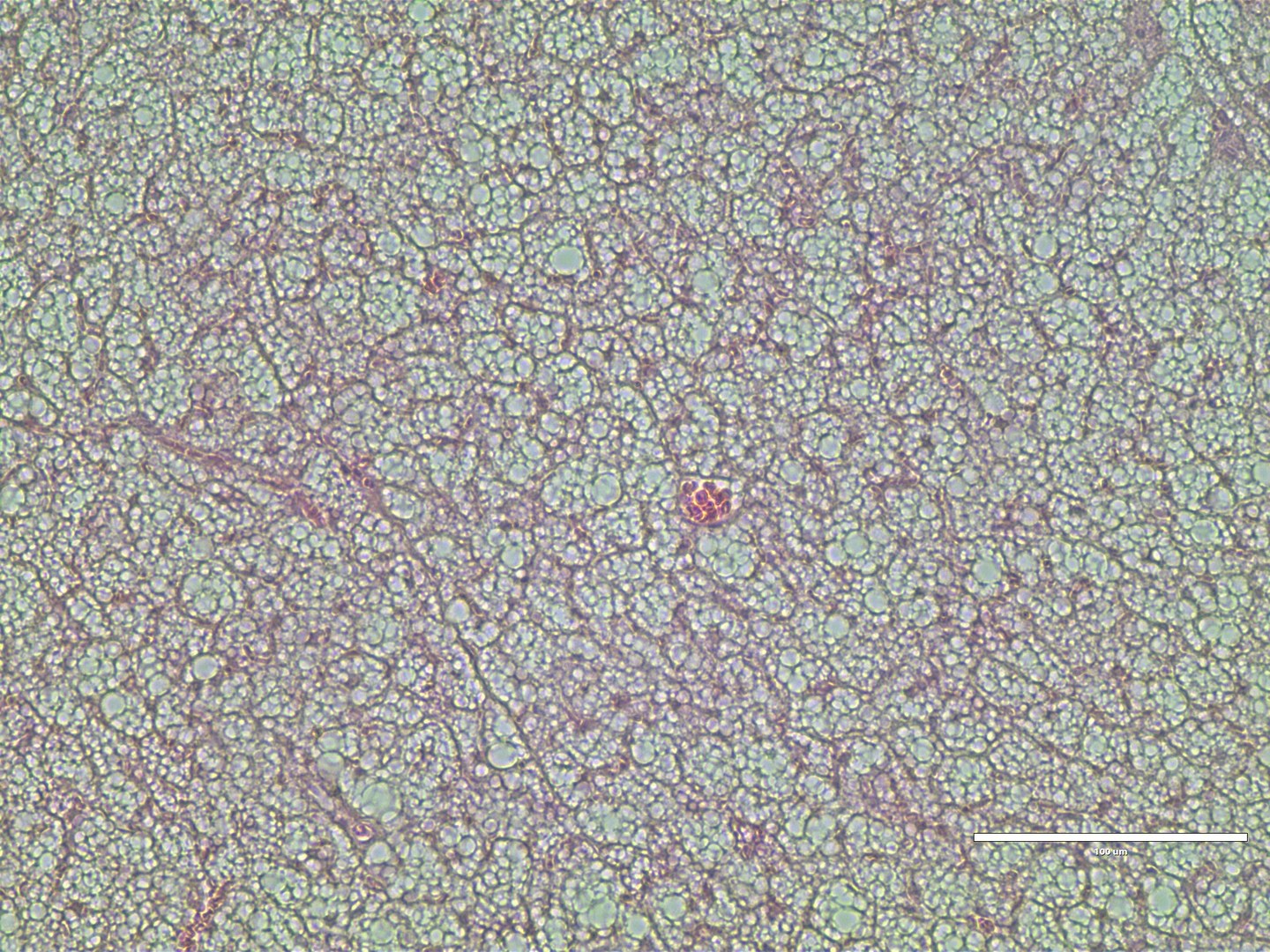
In the picture on the right one sees brown adipose tissue after twelve weeks of high fat diet (HE stain).
Viral vectors and nanomedicine
Viral gene transfer
Our goal is to combine modern virology with gene transfer technology.
Lentiviral vectors are promising tools for both molecular biology and gene therapy. Lentiviruses are capable of transducing nondividing cells in vitro and in vivo, e.g. neurons, hepatocytes, and skeletal muscle cells.
Additionally, these vectors can be used for gene transfer into embryonal stem cells (ES-cells). We and others have established methods that enable the use of lentiviral vectors for the generation of transgenic animals (lentiviral transgenesis). The transduction of pre-implantation embryos with lentiviral vectors results in the expression of transgenes during embryogenesis as well as in newborn and adult animals. Lentiviral transgenesis has already been established for several species of animals, including mice, pigs, rats, cows, and chickens.
Nanomedicine
Our goal is the development of nanotechnology-based strategies for targeted gene transfer for use in innovative therapies, such as the transfer of genetic material or genetically modified stem- and progenitor cells to the cardiovascular and central nervous systems. This work is being done as part of the DFG-funded research group FOR 917 “Nanoguide”.
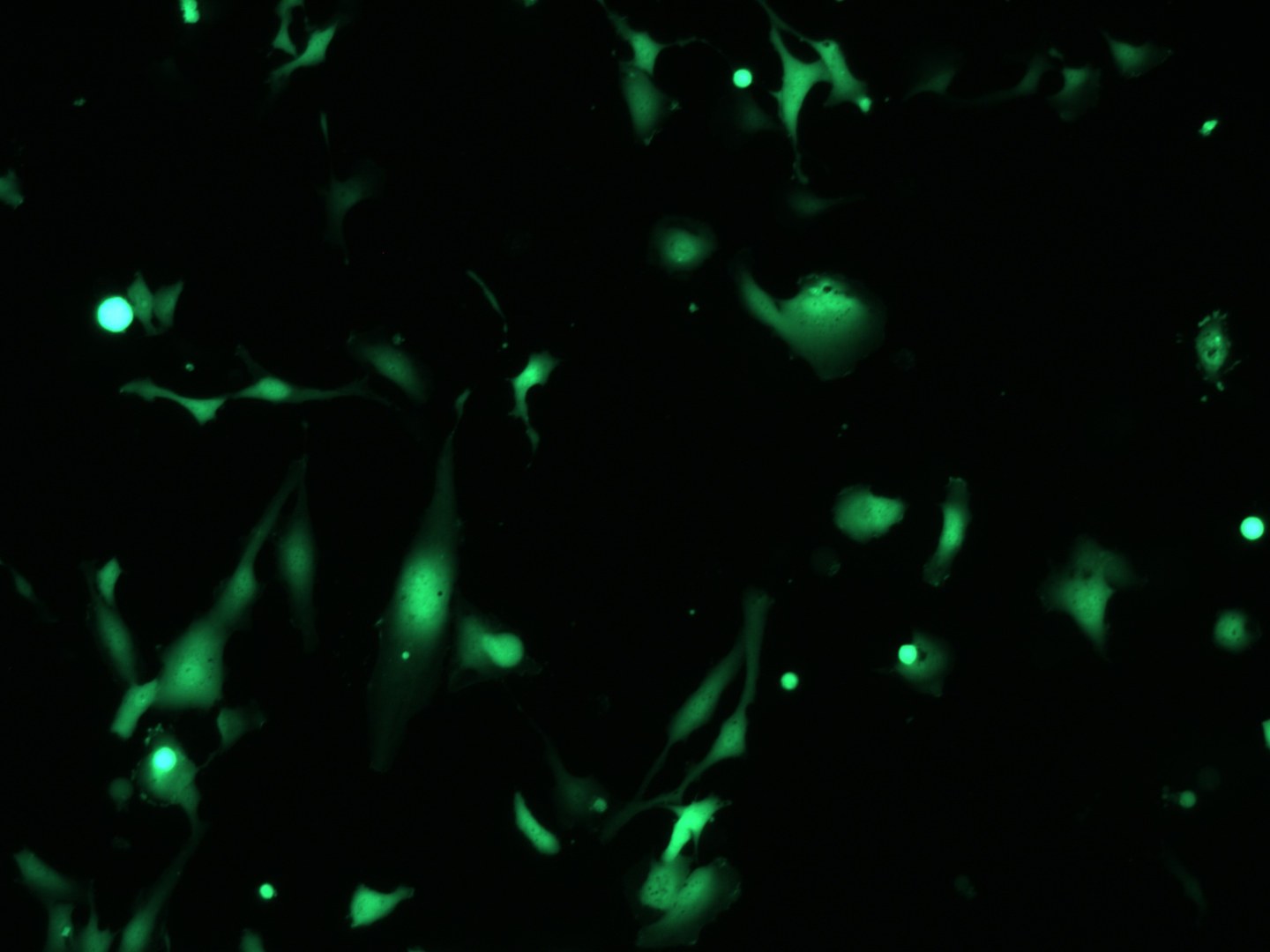
In the left picture: we transduced GFP-expressing smooth muscle cells with magnetic nanoparticle-coupled lentiviral particles.
GPCR and purine signaling
G protein-coupled receptors regulate a plethora of physiological processes. Moreover, these receptors and their ligands are the targets for the majority of currently approved pharmaceuticals. We investigate GPCRs, their ligands and the associated signal transduction cascades primarily in the context of energy homeostasis, metabolism and the cardiovascular system.
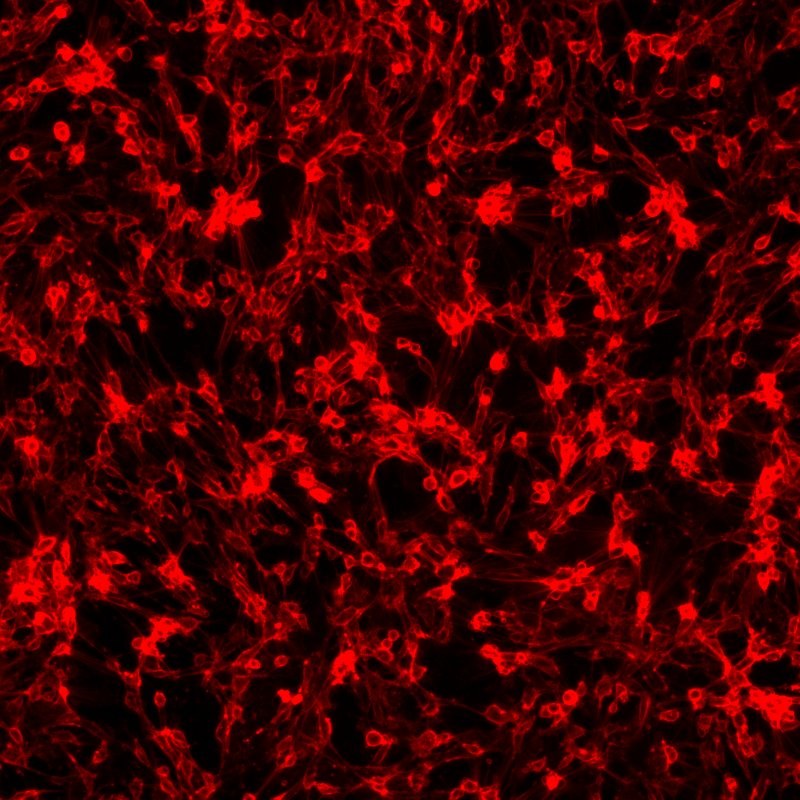
In the picture on the right one can see immunocytochemical staining of primary murine white pre-adipocytes detected with a primary antibody against Gpr81 and a secondary antibody labelled with Alexa Fluor 647.
NO/cGMP signaling
cGMP is an important second messenger and mediates the biological effects of nitric oxide (NO) and natriuretic peptides (such as atrial natriuretic peptide). The cGMP signaling pathway plays a prominent role in regulating the contraction of smooth vascular muscles and thus blood pressure. Furthermore, cGMP regulates a multitude of additional biological processes. We are particularly interested in the function of the cGMP signaling pathway in adipocytes and in metabolism. To study these processes, we utilize, among traditional biochemical approaches, genetically encoded fluorescent biosensors (such as Förster-Resonance-Energy-Transfer = FRET biosensor) and single fluorophore biosensors.
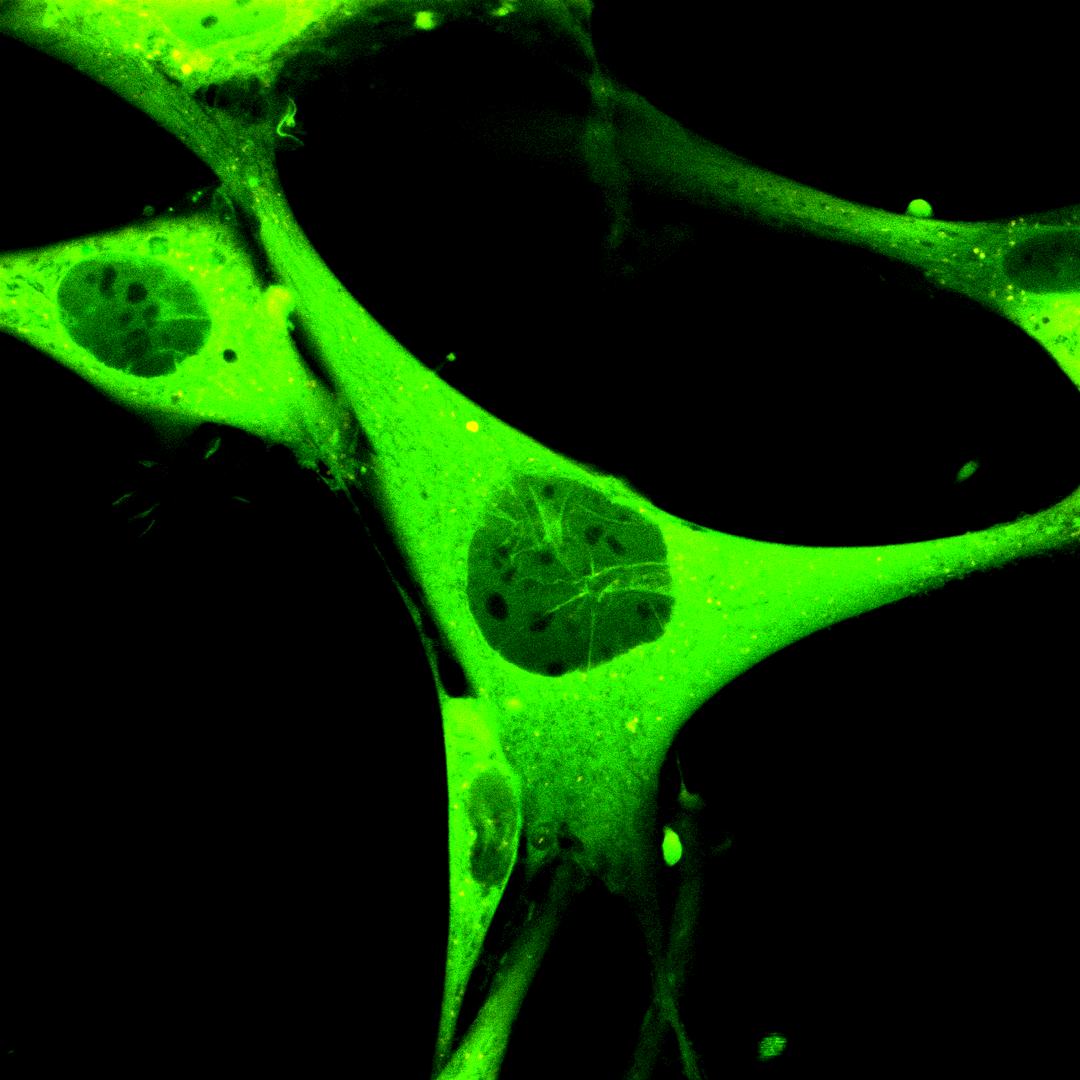
Displayed on the left is a brown adipocyte progenitor cell (pre brown adipocyte) isolated from a transgenic mouse strain, ubiquitously expressing the cGi-500 FRET biosensor.
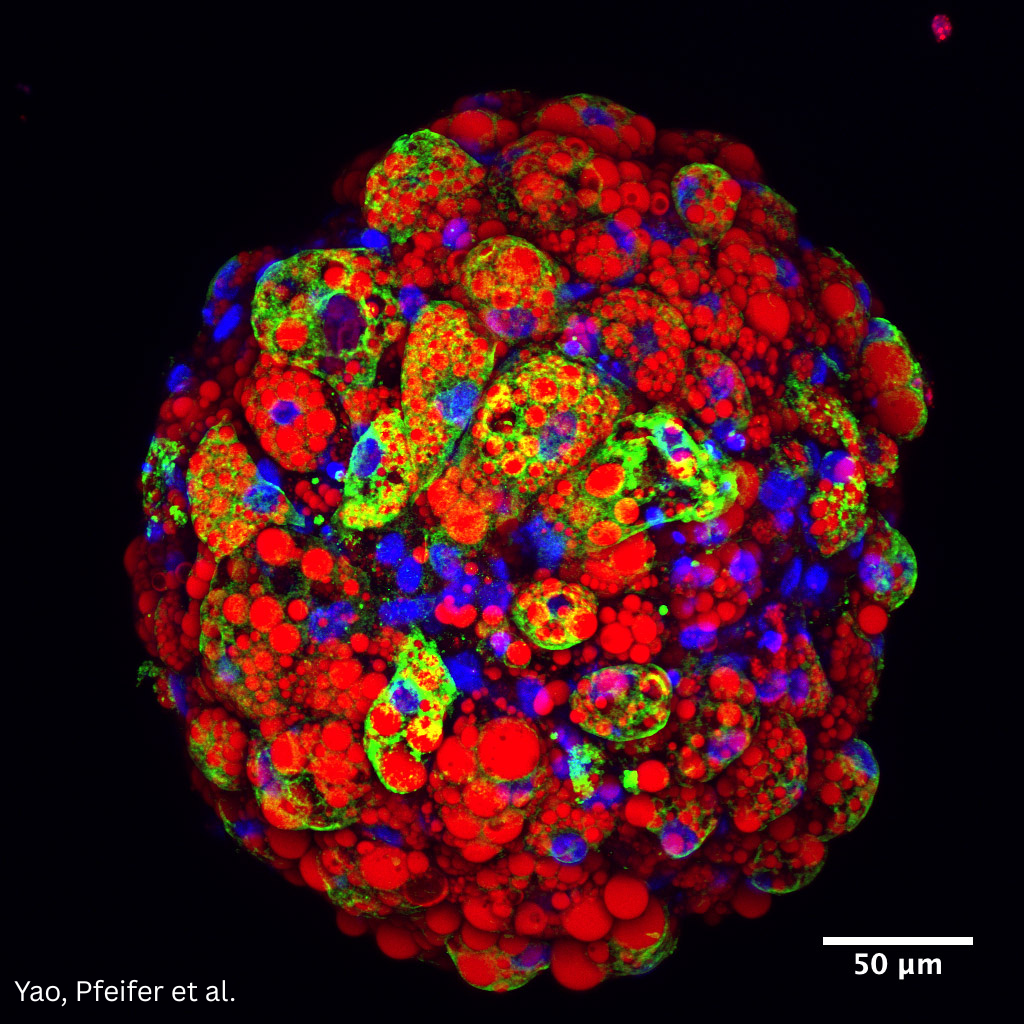
hiPSC derived brown adipose organoids
We aim to use hiPSC derived brown adipose organoids (hiPSC-BAOs) as in vitro models to study human brown adipose tissue (hBAT) metabolism. We are especially interested in regulation of thermogenesis in hiPSC-BAOs and crosstalk between different cell types within hiPSC-BAO. See also Reverte et al. Nature Cell Biology 2024 DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-023-01311-9
Figure: hiPSC-BAO with UCP1 in green, Oil red O in red and DAPI in blue.
Alexander Pfeifer has a long-standing interest in cellular signaling, molecular pharmacology and academic drug research. He has been doing pioneering work in the field of purinergic signaling and the NO/cGMP pathway as well as contributed to the field of G-protein coupled receptors. For several years, his workgroup studies these pharmacologically important signaling pathways to identify drug targets and to develop novel therapeutic approaches. A major focus of their research lies on metabolic diseases and energy homeostasis. He is speaker of the DFG-funded Collaborative Research Center CRC/TRR333 “BATenergy”.
Another important topic of their research is gene and drug delivery, where the workgroup focuses on lentiviral vectors and nanoparticles to deliver genetic material and drug molecules respectively, to target specific cells and tissues. Prof. Pfeifer was also the speaker of the DFG Research Unit FOR917 and the DAAD Strategic Network Europe-Japan on multimodal nanoparticles.

Nature Cell Biology
EPAC1 enhances brown fat growth and beige adipogenesis
Reverte-Salisa, L., Siddig, S., Hildebrand, S. et al. EPAC1 enhances brown fat growth and beige adipogenesis. Nat Cell Biol 26, 113–123 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-023-01311-9
Nature
Brown adipose tissue (BAT) dissipates energy and promotes cardio-metabolic health. In this publication, Nieman et al identifiy inosine as novel tissue-messenger in brown fat (BAT). They show that treatment of mice with inosine increased BAT-dependent energy expenditure and induced “browning” of white adipose tissue. This work is funded by the DFG.
Niemann, B., Haufs-Brusberg, S., Puetz, L. et al. Apoptotic brown adipocytes enhance energy expenditure via extracellular inosine. Nature (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05041-0
Communications Biology
Copperi F, Schleis I, Roumain M, Muccioli GG, Casola S, Klingenspor M, Pfeifer A, Gnad T. EBI2 is a negative modulator of brown adipose tissue energy expenditure in mice and human brown adipocytes.
Commun Biol. 2022 Mar 29;5(1):280. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03201-6. PMID: 35351968
Communications Biology
Hildebrand S, Ibrahim M, Schlitzer A, Maegdefessel L, Röll W, Pfeifer A. PDGF regulates guanylate cyclase expression and cGMP signaling in vascular smooth muscle.
Commun Biol. 2022 Mar 3;5(1):197. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03140-2. PMID: 35241778
Cell
Sveidahl Johansen O, Ma T, Hansen JB, Markussen LK, Schreiber R, Reverte-Salisa L, Dong H, Christensen DP, Sun W, Gnad T, Karavaeva I, Nielsen TS, Kooijman S, Cero C, Dmytriyeva O, Shen Y, Razzoli M, O'Brien SL, Kuipers EN, Nielsen CH, Orchard W, Willemsen N, Jespersen NZ, Lundh M, Sustarsic EG, Hallgren CM, Frost M, McGonigle S, Isidor MS, Broholm C, Pedersen O, Hansen JB, Grarup N, Hansen T, Kjær A, Granneman JG, Babu MM, Calebiro D, Nielsen S, Rydén M, Soccio R, Rensen PCN, Treebak JT, Schwartz TW, Emanuelli B, Bartolomucci A, Pfeifer A, Zechner R, Scheele C, Mandrup S, Gerhart-Hines Z. Lipolysis drives expression of the constitutively active receptor GPR3 to induce adipose thermogenesis.
Cell. 2021 Jun 24;184(13):3502-3518.e33. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.04.037. Epub 2021
ACS Nano
Hildebrand S, Löwa N, Paysen H, Fratila RM, Reverte-Salisa L, Trakoolwilaiwan T, Niu Z, Kasparis G, Preuss SF, Kosch O, M de la Fuente J, Thanh NTK, Wiekhorst F, Pfeifer A. Quantification of Lipoprotein Uptake in Vivo Using Magnetic Particle Imaging and Spectroscopy.
ACS Nano. 2021 Jan 26;15(1):434-446. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c03229. Epub 2020 Dec
Cell Metabolism
Gnad T, Navarro G, Lahesmaa M, Reverte-Salisa L, Copperi F, Cordomi A, Naumann J, Hochhäuser A, Haufs-Brusberg S, Wenzel D, Suhr F, Jespersen NZ, Scheele C, Tsvilovskyy V, Brinkmann C, Rittweger J, Dani C, Kranz M, Deuther-Conrad W, Eltzschig HK, Niemi T, Taittonen M, Brust P, Nuutila P, Pardo L, Fleischmann BK, Blüher M, Franco R, Bloch W, Virtanen KA, Pfeifer A. Adenosine/A2B Receptor Signaling Ameliorates the Effects of Aging and Counteracts Obesity.
Cell Metab. 2020 Jul 7;32(1):56-70.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.06.006. Epub 2020 Jun
Nature
Sukonina V, Ma H, Zhang W, Bartesaghi S, Subhash S, Heglind M, Foyn H, Betz MJ, Nilsson D, Lidell ME, Naumann J, Haufs-Brusberg S, Palmgren H, Mondal T, Beg M, Jedrychowski MP, Taskén K, Pfeifer A, Peng XR, Kanduri C, Enerbäck S.
FOXK1 and FOXK2 regulate aerobic glycolysis
Nature. 2019 Feb;566(7743):279-283. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-0900-5. Epub 2019 Jan
Nature Communications
Chen Y, Buyel JJ*, Hanssen MJ, Siegel F, Pan R, Naumann J, Schell M, van der Lans A, Schlein C, Froehlich H, Heeren J, Virtanen KA, van Marken Lichtenbelt W, Pfeifer A. Exosomal microRNA miR-92a concentration in serum reflects human brown fat activity.
Nat Commun. 2016 Apr 27;7:11420. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11420.
Nature Communications
Hoffmann LS, Etzrodt J, Willkomm L, Sanyal A, Scheja L, Fischer AWC, Stasch JP, Bloch W, Friebe A, Heeren J, Pfeifer A. Stimulation of soluble guanylyl cyclase protects against obesity by recruiting brown adipose tissue.
Nat Commun. 2015 May 26;6:7235. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8235
Nature Communications
Chen Y, Siegel F, Kipschull S, Haas B, Fröhlich H, Meister G, Pfeifer A. miR-155 regulates differentiation of brown and beige adipocytes via a bistable circuit.
Nat Commun. 2013;4:1769.
Come join us! We are always looking for enthusiastic candidates for internships, master thesis, PhD and Postdoc projects. Please feel free to contact us any time!
For currently available open positions please check here
Contact
Prof. Dr. Alexander Pfeifer
Venusberg Campus 1
53127 Bonn


